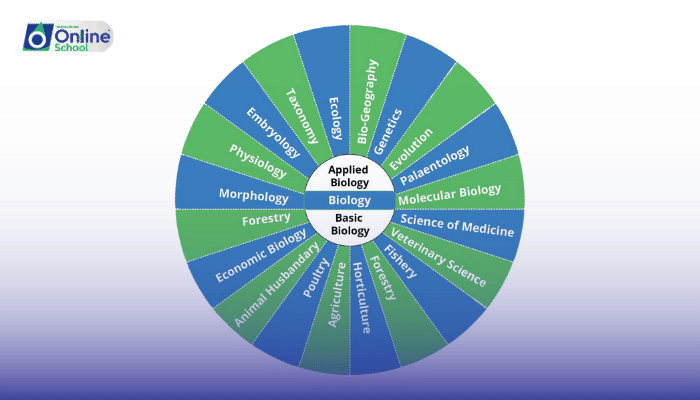
Learning Objectives:
i. Understand and define the branches of biology: morphology, anatomy, physiology, embryology, and others.
ii. Highlight the unique focus and importance of each branch in the study of life.
Content:
I. Morphology:
Definition: Morphology is the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features.
Focus: It deals with the outward appearance (shape, structure, color, pattern) of organisms and their parts.
II. Anatomy:
Definition: Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts.
Focus: It involves dissecting and studying the structural organization of living things.
III. Physiology:
Definition: Physiology is the scientific study of the functions and mechanisms in a living system.
Focus: It explores how organisms, organ systems, organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemical or physical functions that exist in a living system.
IV. Embryology:
Definition: Embryology is the branch of biology that studies the prenatal development of gametes (sex cells), fertilization, and development of embryos and fetuses.
Focus: Additionally, it encompasses the study of congenital disorders that occur before birth.
V. Additional Branches: Briefly introduce other branches such as taxonomy, cell biology, histology, and genetics, outlining their primary focus.
Important Questions for Self-Study:
i. Define morphology and give an example of how it is applied in the study of living organisms.
ii. How does anatomy differ from morphology, and why is it important?
iii. Explain the role of physiology in understanding the functions of different body systems.
iv. Describe the process studied by embryology and its significance in biology.
v. Why is it important for a biologist to have knowledge of different branches like taxonomy and genetics?
vi. How do the branches of biology such as cell biology and histology complement the study of anatomy and physiology?
vii. What are some of the practical applications of understanding the structure and function of living organisms?
viii. In what ways can the study of physiology inform our understanding of health and disease?
ix. How has the field of embryology contributed to medical science, especially in the context of reproductive health?
x. Choose one additional branch of biology not covered in detail during the lesson. What is its focus, and why is it important?